Can We Make Ipv4 Great Again?

The Internet Assigned Name Authority IANA) handed out the Terminal IPv4 address space in Feb of 2011. The Internet'southward ability to function is predicated upon each device having a unique Net Protocol (IP) address and thus, a new address schema chosen IP version 6, or IPv6, was implemented and so that the ever-growing number of "things" on the Internet tin can office properly. In the time since the IANA handed out the final IPv4 address space, the price of IPv4 addresses has skyrocketed. This increasingly unnecessary expense can be a brunt for companies that have not fabricated the switch to IPv6.
Background: IPv4 – IPv6, What does this mean?
TCP/IP is the technology that devices use to interact online. What allows each device to get online and communicate is that each 1 has an unique IP address. IP addresses enable each device to interact with each other over the Global Internet. From desktops to laptops, to PS4s, to cell phones, to airplanes, to IP enabled washers and dryers, well-nigh things will exist connected online – this ways we need a lot more addresses than are available today.
At the inception of the Net, IP version 4 (IPv4) was and is currently the most widespread protocol used to communicate. Past their binary nature, IP addresses are a finite resource and Vint & Bob established, at the fourth dimension, ii^32 unique IP Addresses or ~ 4.iii Billion addresses. While 4.three Billion might seem like a vast number, the growing amount of Internet participation has exhausted this supply – in fact, it has been predicted that past 2030, there will exist more than 15 Internet-enabled devices for every man, adult female, and child on planet earth. In February 2011, the keeper of the gratuitous address puddle, the Internet Assigned Numbers Authority, (IANA), fully wearied and allocated all of the IPv4 Addresses.[1]
To go on the operation of the Net, Internet Protocol version vi (IPv6) was created. The accost space created in IPv6 is mind-bogglingly vast –2^128 or more 170 undecillion addresses. Such an astronomical number of addresses is unlikely to exist depleted in the next 50 years.Everything online must transition to include both IPv6 and IPv4 (a state called "dual stack") and somewhen transition entirely to the new IPv6 protocol. There are already IPv6-simply networks existence deployed equally the cost/overhead of getting IPv4 resources is non worth the hassle. For the curious, we create the following video to give yous a feel for the size of the IPv6 address space:
IPv6 was created in the mid-'90s as a consequence of engineering efforts to keep the Net growing. It is an entirely new protocol that is not "backward compatible" with IPv4. However, both protocols can run simultaneously over the same "wires". This means that there will exist a progressive transition (picking up pace from this point forward) from IPv4 to IPv6 commencing with devices that support both protocols (likewise known equally dual stacking). Eventually, IPv4 will end to be supported and in the cease,all IPv4 only devices will no longer be able to communicate with the IPv6 enabled Net. Why end support of IPv4? Take a guess – who wants to manage 2 network protocols for every IP addressable object? As IPv6 deployments increment over time, the natural next step will be reducing the role of IPv4 both in front cease applications as well as dorsum end management networks.
Thankfully, the transition to IPv6 has been underway for a while now. Every bit of May of 2019, the overall adoption of IPv6 worldwide was 27%, while IPv6 adoption in the United states of america was at 34%. Germany was ahead of the pack with 41%. This page has up-to-date statistics for IPv6 adoption.
How the Internet is "Inter" connected.
To understand how nosotros volition exist afflicted, information technology is helpful to understand how the Internet is actually "inter-connected". The Internet is literally a "web" of networks all connected to each other. From our home network that has 2 or 3 computers to Net Service Providers to online companies similar Amazon & eBay.
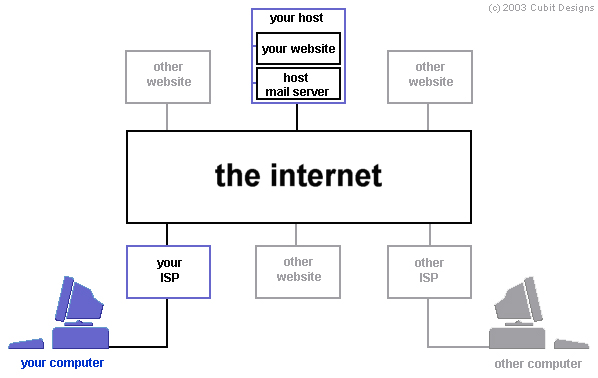
In the middle of this diagram, the "Net" is a collection of all the globe's networks interconnected together so that nosotros, an end-user, can become from point A to signal B beyond (or "routed" beyond) all of these networks. In the end, this means that everyone online and everyone who wants to be online will be undergoing the upgrade to IPv6 starting with getting a new IPv6 address.
At the end of the mean solar day, the biggest and virtually noticeable deviation between IPv4 and IPv6 are the bodily IP Addresses being used. IPv4 had a 32-bit string of numbers that often looked like the following:
202.127.212.134.
This "accost" was a office of a pool of addresses managed by IANA as described earlier. As this address pool has been depleted, all new requests for addresses will merely exist able to go a v6 address. IPv6 addresses are quite a bit more complex – they are 128-fleck addresses:
3ffe:1900:4545:3:200:f8ff:fe21:67cf.
There are many advantages to this more complex accost schema in add-on to the fact that at present every device will take its own unique identifier. Ironically, the longer address will really aid to improve cease-user experience online as the Internet architecture will see improvements with respect to traffic congestion, application specificity[3], security and much more than.
Of course, it's uncommon to use IP addresses direct. Instead, we use a Domain Proper noun Organization (DNS) to translate domain names into the correct IP address. IPv4 uses something called A records to map IPv4 addresses to domain names, and, similarly, IPv6 uses something called AAAA records. This allows you to enter a simple URL then be automatically routed to the correct IP address – all behind the scenes.
We have established that every Internet-enabled device must take a unique IP address. Now, what does this mean for the various constituencies accessing the Cyberspace?
For almost stop-users at home (or mobile users),[four] this transition will happen automatically and volition be mostly unnoticeable. They will get their current and updated addresses from their Internet access provider; businesses will have their It departments configure their ain networks so that their customers (the business organization) volition automatically get their addresses, etc.Therefore, those most concerned about this transformation are those that really manage portions of the Internet: Internet Service Providers, I/PaaS providers, online Content & Application Service providers, and minor to Enterprise businesses that run their own networks.
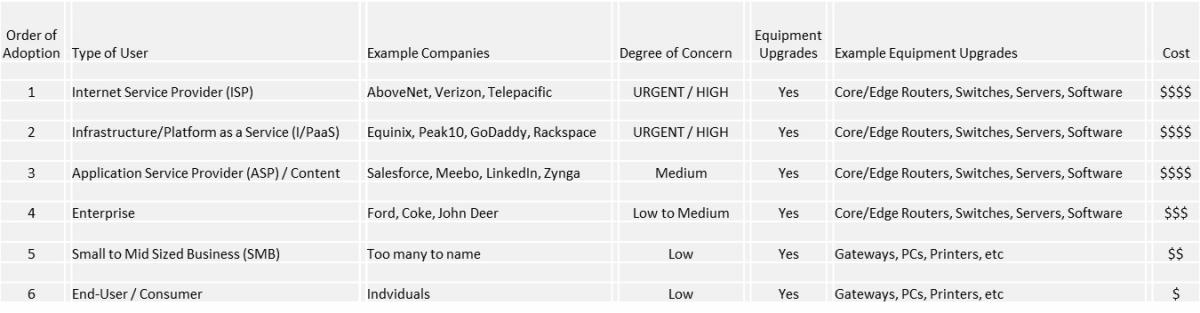
As nosotros see from the higher up nautical chart, most terminate-users and small businesses will really only exist responsible for ensuring that they have purchased IPv6 enabled devices, including computers, wireless access points, smartphones, printers, and game consoles. Virtually devices purchased later 2007 are in fact IPv6 enabled. For example, Microsoft has been IPv6 enabled since version Windows XP-SP1 likewise as commensurate Apple tree OSs.
The heavy lifting will be shouldered by the ISPs, I/PaaS, Content/ASPs and businesses that manage their own networks.
In that location are approximately 66,000 registered Democratic Systems (Equally)[five]. These "networks" are run by ISPs, I/PaaS, ASP/Content as well as government & instruction organizations. All of these "networks" imply a level of cocky-administration, hence Democratic, and will require their Network Administrators to follow this elementary review:
a. Appraise the network for IPv4 just devices, dual stacked devices (IPv4 & IPv6), as well as IPv6 only devices (not many of these yet)
b. Layout an IPv6 network architecture starting with an Address Schema (which entails sub-netting)
c. Determine your "end-gap" measures for IPv4 only devices – at that place are many "translation" scenarios that tin exist employed temporarily to ease burden of next pace – however, one should note that like 8 rails tapes used for playing music, using IPv4 only will impact your Internet feel and over fourth dimension stop to operate[6]
d. Provide a rip/replace plan for those things not capable of supporting IPv6
e. Commence upgrade
These are certainly not petty steps in transitioning to v6, however again, these are sectional to service providers, those direct involved in managing networks. It does not preclude end users or SMB however, from beingness aware of this change and ensuring their own devices are compatible.
Then hopefully this section has given a snap-shot of the "Internet Infrastructure Ecosystem" and how each "vertical" will exist afflicted by this transition. Furthermore, while non intended to cry wolf nor claim the Internet will dice, for those who are involved in the upgrade of your own Network this has catalyzed you to commence the transition. Now the next logical question – when do you really need to practise this?
IPv6 Transition: When practise we really need to start?
The transition to IPv6 is well underway and has been fueled by the announcements from the Regional Cyberspace Registries (RIRs) around the world that they ran out of IPv4 addresses reaching total exhaustion. And then how does this interpret into when yous have to get yourself, your business or your organisation ready?
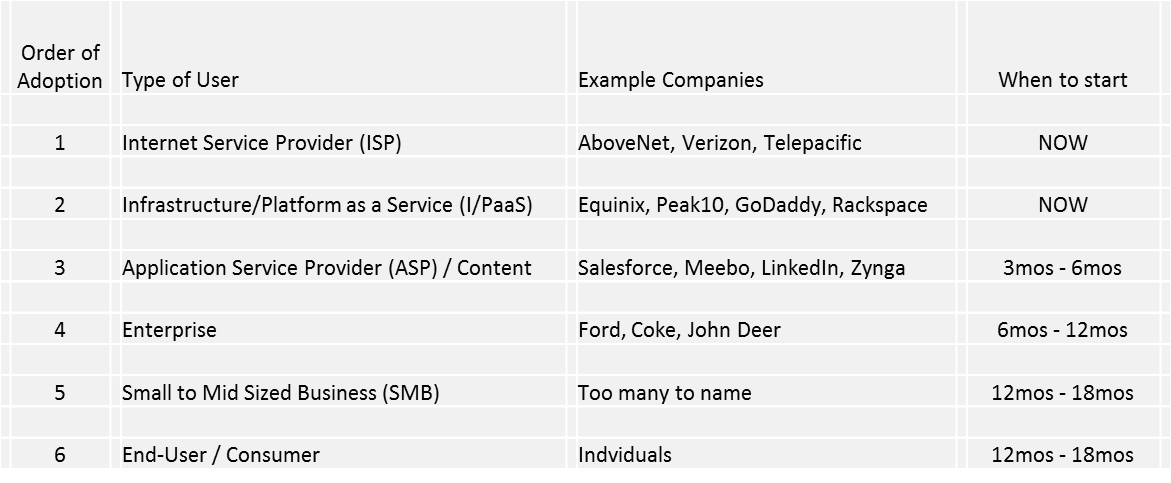
While everyone should be Enlightened that this transition is underway, the "services providers" are really the ones behind the 8ball correct now as it is their jobs to provide Net access or access to Internet infrastructure, which has to exist IPv6 moving forward. Given the lack of backward compatibility, this will require some education, hardware and software upgrades and re-thinking almost how to layout a network. This is due to the fact that the IPv4 mindset was one of "scarce resource" (we will run out of addresses). In an IPv6 world, y'all have nearly unlimited resource and tin plan your network IP Address program very differently.
ISPs, I/PaaS, ASP/Content services providers should be in the midst of transition and if they are not, now is the time to get it moving. Enterprises will take to assess their own network needs but it is non of firsthand urgency – their challenge is that their employees are most probable already using IPv6 in their home environments. And, finally, SMBs and End-Users volition really only take to track their own ISPs steps to upgrade to IPv6 likewise as be aware of existing and future tech purchases existence IPv6 ready.
The entire Internet should run more smoothly and deeply thanks to IPv6
The steps those undertaking this transition volition demand to make are as well a GREAT OPPORTUNITY to automate many rote network processes. The general steps, and where automation tin play a significant role are every bit follows:
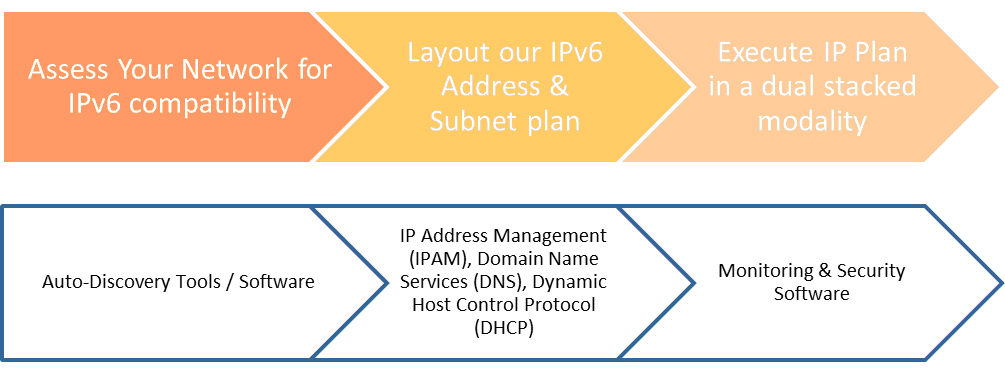
In subsequent articles we will be diving into Software Tools to help Service providers in this transition, what some of the emerging all-time practices will exist in the areas of IPv6 Automation, IPv6 Security, and IPv6 as information technology relates to Asset Tracking.
For more information please read our IPv6 FAQ.
________________
[1]The Asia Pacific Regional Internet Registry, one of the 5 regional registries that study to IANA, is too fully depleted of IPv4 resources every bit of April 2011.
[2]Come across: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/List_of_Internet_top-level_domains
[3]A reference to geo-location as a role of many cease-users' application experience.
[four]Stop-users who have home networks that connect more than than ane auto will still need to ensure that all their devices can back up both IPv4 & IPv6. For example, ensure your Linksys Wireless router tin can back up both protocols.
[5]Wikipedia AS Write-Upward: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Autonomous_system_(Net)
[6]Good examples of IPv6 "translation" end-gap measures: http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/IPv6#Transition_mechanisms
Source: https://www.6connect.com/resources/ipv6-and-the-transition-from-ipv4-explained/
0 Response to "Can We Make Ipv4 Great Again?"
Publicar un comentario